[ad_1]

Android malware builders are stepping up their billing fraud recreation with apps that disable Wi-Fi connections, surreptitiously subscribe customers to expensive wi-fi providers, and intercept textual content messages, all in a bid to gather hefty charges from unsuspecting customers, Microsoft stated on Friday.
This risk class has been a truth of life on the Android platform for years, as exemplified by a household of malware referred to as Joker, which has contaminated tens of millions of telephones since 2016. Regardless of consciousness of the issue, little consideration has been paid to the methods that such “toll fraud” malware makes use of. Enter Microsoft, which has revealed a technical deep dive on the issue.
The billing mechanism abused in this sort of fraud is WAP, brief for wi-fi utility protocol, which offers a method of accessing data over a cellular community. Cell phone customers can subscribe to such providers by visiting a service supplier’s net web page whereas their gadgets are related to mobile service, then clicking a button. In some instances, the provider will reply by texting a one-time password (OTP) to the telephone and requiring the consumer to ship it again as a way to confirm the subscription request. The method seems to be like this:
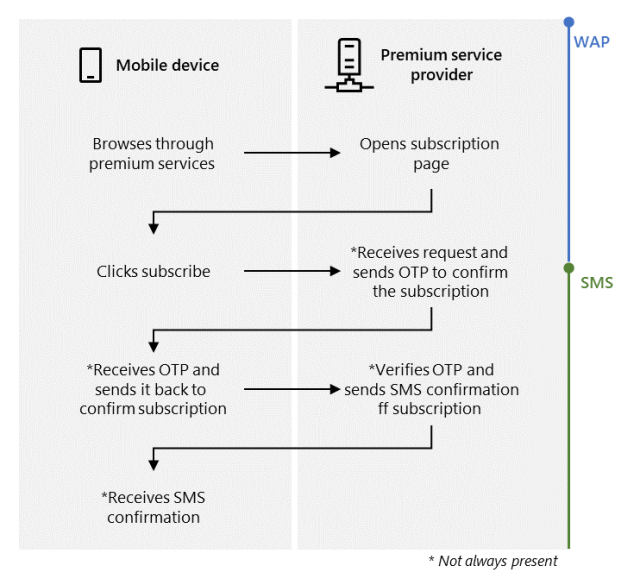
Microsoft
The objective of the malicious apps is to subscribe contaminated telephones to those WAP providers mechanically, with out the discover or consent of the proprietor. Microsoft stated that malicious Android apps its researchers have analyzed obtain this objective by following these steps:
- Disable the Wi-Fi connection or await the consumer to modify to a cellular community
- Silently navigate to the subscription web page
- Auto-click the subscription button
- Intercept the OTP (if relevant)
- Ship the OTP to the service supplier (if relevant)
- Cancel the SMS notifications (if relevant)
Malware builders have varied methods to power a telephone to make use of a mobile connection even when it’s related to Wi-Fi. On gadgets operating Android 9 or earlier, the builders can invoke the setWifiEnabled methodology of the WifiManager class. For variations 10 and above, builders can use the requestNetwork perform of the ConnectivityManager class. Finally, telephones will load knowledge completely over the mobile community, as demonstrated on this picture:
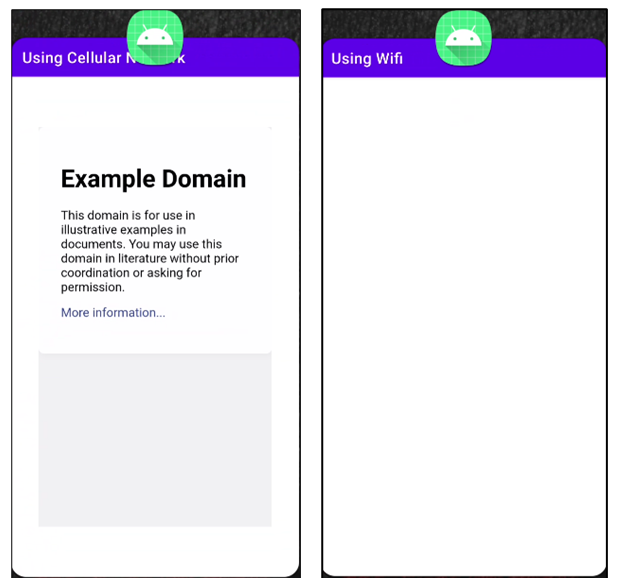
Microsoft
As soon as a telephone makes use of the mobile community for knowledge transmission, the malicious app surreptitiously opens a browser within the background, navigates to the WAP subscription web page, and clicks a subscribe button. Confirming the subscription could be tough as a result of affirmation prompts can come by SMS, HTTP, or USSD protocols. Microsoft lays out particular strategies that malware builders can use to bypass every kind of affirmation. The Microsoft put up then goes on to elucidate how the malware suppresses periodic messages that the subscription service could ship the consumer to remind them of their subscription.
“By subscribing customers to premium providers, this malware can result in victims receiving vital cellular invoice costs,” Microsoft researchers wrote. “Affected gadgets even have elevated danger as a result of this risk manages to evade detection and might obtain a excessive variety of installations earlier than a single variant will get eliminated.”
Google actively bars apps from its Play market when it detects indicators of fraud or malice, or when it receives studies of malicious apps from third events. Whereas Google typically doesn’t take away malicious apps till after they’ve contaminated tens of millions of customers, apps downloaded from Play are typically considered extra reliable than apps from third-party markets.
Source link


